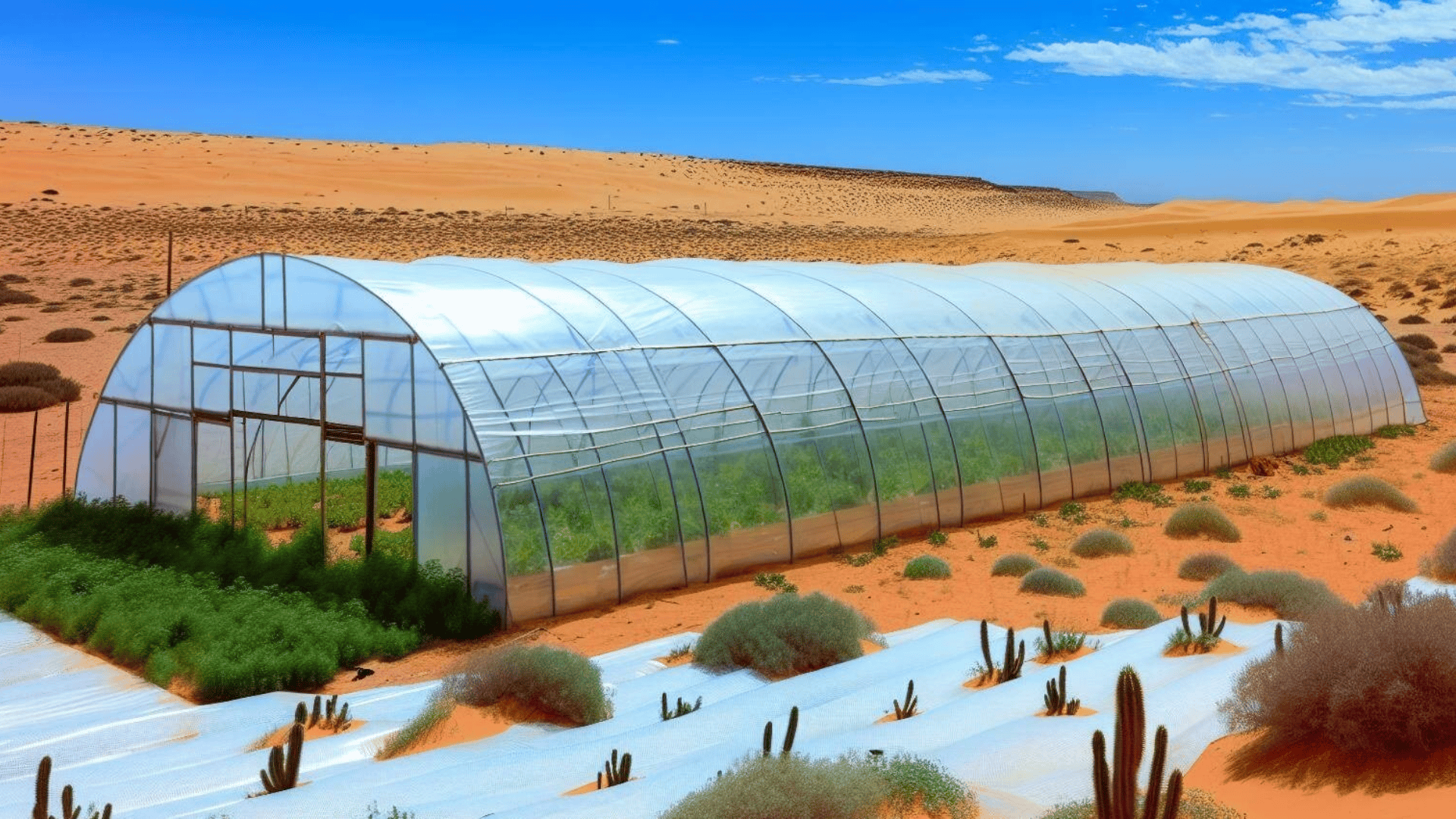
In the Middle East and North Africa (MENA), where arable land is scarce and water is even scarcer, agriculture faces significant challenges. With 85% of its food imported, the region’s dependence on external food sources is among the highest globally. However, a technological revolution is underway, aiming to transform these challenges into opportunities through AgriTech innovations.
Why AgriTech Matters in MENA
The region’s unique constraints—only 5% arable land and severe water scarcity—necessitate innovative approaches to agriculture. AgriTech offers solutions like vertical farming, hydroponics, and precision agriculture that significantly reduce water use and increase land efficiency, making them ideal for MENA’s arid conditions.
Current Market Overview
The AgriTech landscape in MENA is marked by a diverse array of initiatives tailored to tackle the specific challenges of each country:
- United Arab Emirates (UAE): A leader in AgriTech adoption, the UAE has spearheaded numerous initiatives like Emirates Bio Farm and Pure Harvest Smart Farms, setting benchmarks in sustainable and high-tech farming practices.
- Saudi Arabia: With its Vision 2030, Saudi Arabia is focusing on enhancing food security through investments in sustainable farming and food production technologies, aiming to reduce its dependence on food imports.
- Egypt: As the agricultural hub of MENA, Egypt plays a critical role, contributing 11% to its GDP and employing 28% of the workforce. The country is focusing on integrating more technology into its farming practices to increase efficiency and output.
Spotlight on Technological Innovations
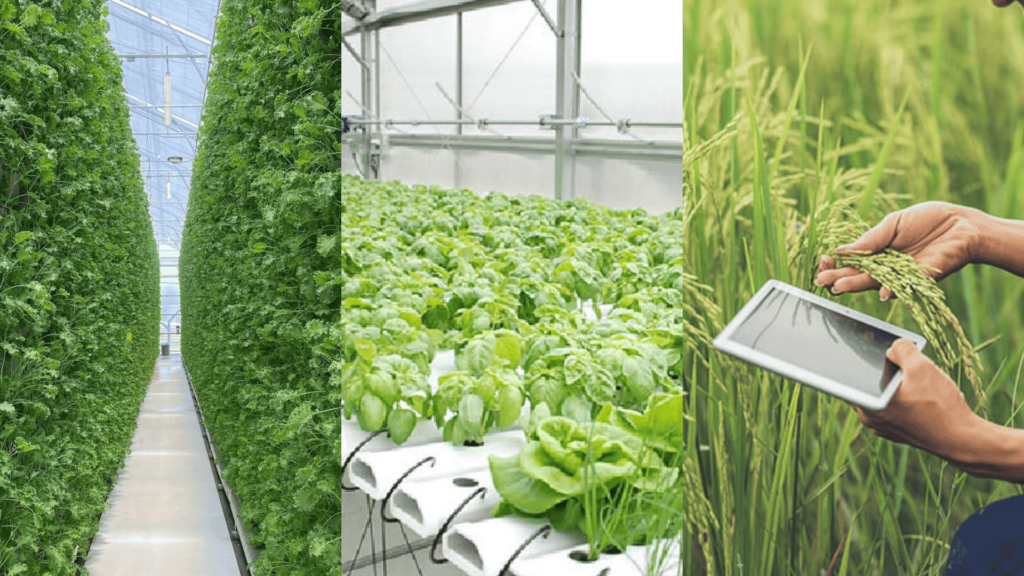

- Vertical Farming:
- Bustanica in the UAE is a flagship project producing over a million kilograms of leafy greens annually in a controlled indoor environment. This method conserves water and optimizes space.
- Red Sea Farms in Saudi Arabia integrates solar-powered systems to reduce water usage, demonstrating how vertical farming can excel in desert climates.
- Hydroponics:
- Hydroponics is a soil-less farming technique that is increasingly popular across MENA for its water efficiency and high yield per square meter. Projects like Jordan’s GreenCo and Egypt’s Cairo Greens are leading the way in this innovative farming method.
- Precision Agriculture and IoT:
- Technologies such as AI, drones, and IoT are reshaping MENA’s agriculture. For example, the King Abdullah Initiative in Saudi Arabia uses AI-powered irrigation systems to enhance water efficiency.
- In Egypt, IoT sensors monitor soil moisture and weather conditions in real time, helping farmers optimize water use and crop growth.
Investment Trends
Investment in MENA’s AgriTech sector reached $1.9 billion in 2023, with significant contributions from government subsidies and public-private partnerships. These investments focus on sustainable farming and digital platforms to improve the efficiency and sustainability of agriculture in the region.
Government Policies and Initiatives

Governments across MENA are implementing strong policy frameworks to support the growth of AgriTech. Notable initiatives include:
- Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030: Aims at transforming agriculture through technology, promoting sustainable farming methods to ensure food security.
- UAE’s National Food Security Strategy 2051: Focuses on using cutting-edge technologies to boost local food production and make the UAE a world leader in the field of innovative food security solutions.
- Qatar and Egypt: These countries are supporting AgriTech startups through funding, incubators, and accelerators, driving innovation in the sector.
Case Studies: AgriTech Success Stories
- Nabt (Saudi Arabia): A precision agriculture startup that utilizes AI and IoT to optimize crop management. In 2024, Nabt secured $1.5 million in seed funding to expand their operations and enhance yields across Saudi farms.
- Viridia Tech (Egypt): Focused on sustainable farming, this startup won a $100,000 grand prize at the Mega Green Accelerator for its innovations in water-efficient technologies.
- FarmERP (UAE): Specializes in technology solutions for agriculture and supply chain management, receiving the UAE Technology Excellence Award in Agritech for its impact in advancing sustainable agricultural practices.
Challenges and Opportunities in MENA’s AgriTech Sector
Challenges
The AgriTech sector in the MENA region faces several critical challenges that could impede its progress if not adequately addressed:
- Water Scarcity:
Water scarcity remains the most significant challenge, as MENA is one of the most water-stressed regions in the world. Agriculture consumes a vast majority of available freshwater, making water-efficient technologies crucial.
Impact: Despite advances in technology, the finite water resources limit extensive agricultural expansion, and the high cost of desalination and water recycling technologies can be prohibitive.
- Regulatory Barriers:
Inconsistent and sometimes restrictive regulations across different countries in MENA can complicate cross-border operations and the adoption of new technologies.
Impact: These regulatory challenges can deter investment and slow down the deployment of innovative farming technologies, hindering regional integration of AgriTech solutions.
- High Costs of Technology:
The initial setup and ongoing maintenance costs for state-of-the-art AgriTech systems are often high. This includes the costs of AI systems, robotics, and the infrastructure needed for vertical farms and hydroponic systems.
Impact: These costs make it challenging for smaller farms and new startups to adopt advanced technologies, potentially widening the gap between large and small agricultural enterprises.
Opportunities
Despite these challenges, the AgriTech sector in MENA is poised for significant growth, driven by several compelling opportunities:

- Increasing Demand for Local and Sustainable Food Production:
There is a growing consumer preference for locally produced, sustainable food. This trend is driven by increasing awareness of environmental impacts and food safety concerns.
Potential: AgriTech can meet this demand by enhancing local production capabilities, reducing the region’s reliance on imported foods, and improving the overall sustainability of agriculture.
- Government and Private Sector Investment:
Governments across MENA are actively investing in AgriTech as part of broader economic diversification and sustainability goals. This is complemented by private investments and partnerships.
Potential: These investments not only provide the necessary capital to advance technological adoption but also create an enabling environment for innovation and entrepreneurship in agriculture.
- Technological Advancements and Innovation:
Rapid advancements in technologies such as AI, IoT, drones, and robotics offer transformative solutions for agriculture.
Potential: These technologies can drastically improve efficiency and yields, reduce waste, and enable precision agriculture that adapts to the region’s unique climate conditions.
- Collaborative Efforts for Knowledge and Resource Sharing:
International collaborations and partnerships with countries that are leaders in AgriTech can provide valuable knowledge and technology transfer opportunities.
Potential: Such collaborations can accelerate the adoption of best practices and advanced technologies in MENA, boosting the region’s capacity to innovate and adapt to agricultural challenges.
The Future of Food Security in MENA
As MENA increasingly focuses on AgriTech, future trends point towards more controlled-environment agriculture (CEA), use of AI and robotics in farming, and the development of sustainable innovations such as biodegradable packaging and alternative proteins. These advances are setting MENA on a path to becoming a leader in sustainable and efficient agriculture.
Conclusion: A New Era of Farming
AgriTech is crucial for overcoming the agricultural challenges in MENA, transforming the sector into a high-tech, sustainable model that other arid regions around the world might follow. Government support and continuous investment are vital as MENA moves towards a more self-reliant and environmentally sustainable agricultural future.
Checkout our report on Agritech in MENA.